Water-As-A-Fuel Market For The Future Of Clean Energy
By Bhushan Dhumal

The idea of utilizing water as a fuel source has been speculated by scientists, innovators, and researchers from all over the globe, envisioning a world where renewable, green energy can power the planet. However, as the world is evolving from the traditional fossil fuels and looking for cleaner energy sources, water can be a key contributor to ever-increasing energy demands while helping countries achieve climate goals.
Drivers, Barriers, Technological Progress, And Possibilities
Water-to-fuel conversion is truly a revolutionary process that focuses on the decomposition of water molecules in an energyefficient manner. In layman’s terms, water fuel refers to the means of using water as a source of energy, more particularly employing its hydrogen compounds as fuel. Electrolysis is a method used to decompose water into hydrogen and oxygen.
Water is a hydrogen source that contains energy. When burned or introduced into a fuel cell, hydrogen vapor emits water while burning. With the attributes mentioned above, hydrogen is a suitable replacement for fossil fuels. But, hydrogen fuel itself does not come from water. Instead, water is a medium that is used to extract hydrogen in order for hydrogen to be classified as an ecofriendly fuel.
Important Uses Of Water As A Fuel
The potential uses of water-derived hydrogen fuel span across various industries, making it an incredibly versatile energy source.
- Transportation: Hydrogen-powered fuel-cell electric vehicles (EVs) are catching on as a clean option to replace gasoline- and diesel-powered vehicles. Fuel-cell EVs, or FCEVs, can go further than battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and fill up in just a few minutes. This makes them a good fit for long-distance travel and large transporters like trucks, buses, and ships.
- Energy storage: Hydrogen can be stored and used to generate electricity through fuel cells, offering a solution to one of the most significant challenges of renewable energy — intermittency. Excess renewable energy generated during periods of low demand can be used to produce hydrogen, which can then be stored and converted back into electricity when needed, providing a stable and reliable energy supply.
- Industrial use: Industries that require high-temperature processes, such as steel manufacturing, chemical production, and oil refining, are some of the most challenging to decarbonize. Hydrogen can serve as a clean alternative to natural gas and coal in these industries, reducing their carbon footprint.
- Power generation: Hydrogen can be blended with natural gas to reduce emissions from existing power plants. In the future, entire power plants could run solely on hydrogen, generating electricity without any carbon emissions.
- Residential and commercial heating: Hydrogen can be used in fuel cells to provide heating and electricity for homes and businesses. In areas with cold climates, hydrogen could replace natural gas as a clean alternative for heating systems, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges Facing The Water-As-A-Fuel Market
While the potential for water as a fuel is promising, several challenges must be addressed for the market to reach its full potential:
- Cost of production: One of the primary challenges is the cost of producing hydrogen through electrolysis. Currently, producing hydrogen using renewable energy sources is more expensive than fossil-fuel-based hydrogen production. However, as renewable energy costs continue to decrease and electrolyzer technology advances, these costs are expected to come down.
- Infrastructure development: Hydrogen infrastructure, including production facilities, storage, and transportation systems, is still in its early stages. Significant investment is needed to develop a comprehensive hydrogen supply chain, from production to end-use applications.
- Water resource management: Large-scale hydrogen production requires substantial amounts of water, raising concerns about water resource management in areas where water scarcity is a problem. It will be essential to develop water-efficient electrolysis technologies and ensure that hydrogen production does not strain local water supplies.
- Energy productivity: The process of producing hydrogen from water is energy-intensive. A significant amount of energy is lost during electrolysis, transportation, and conversion back into electricity or heat. Improving the overall efficiency of the hydrogen supply chain is crucial for its long-term viability as a clean energy solution.
The Future Of Water As A Fuel
These factors aside, the future of the water-as-a-fuel market is developing.1 Additional investments, technological breakthroughs, and government subsidies ensure that hydrogen will be one of the backbone fuels during the world’s energy transition.
Over the next 10 years, great strides shall be made in electrolyzer tech, the price of renewable energy will fall, and the appropriate bolstering of hydrogen infrastructure will take off. With all these pieces in place, hydrogen will further break out into the wider energy market, forming the base of energy’s future. It will aid in the world’s efforts for decarbonization and support the fight against climate change.
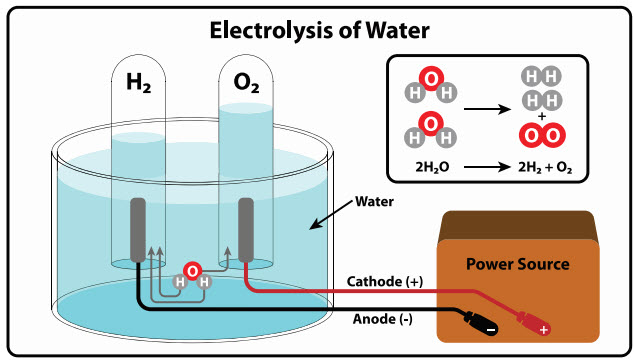
In conclusion, water as a fuel represents an exciting and potentially game-changing development in the energy landscape. By harnessing the power of hydrogen, derived from one of the planet’s most abundant resources, we can unlock a future of clean, renewable, and sustainable energy for generations to come. The water-as-a-fuel market is not just a trend — it’s a vital component of the global shift toward a low-carbon economy.
References:
 About The Author
About The Author
Bhushan Dhumal is a market research professional and industry analyst specializing in emerging technologies, renewable energy, and sustainability trends. With a strong background in market forecasting and strategic analysis, he has contributed to various publications and reports, providing insights into evolving industries.
