Coronavirus And The Water Cycle — Here Is What Treatment Professionals Need To Know
By Nicole McLellan, David Pernitsky, and Arthur Umble
As the global health community tracks the spread of this virus, it’s important for water and wastewater professionals to keep updated on potential impacts.
It's hard to miss the headlines. The recent outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV or COVID-19) has dominated news cycles in recent weeks. The World Health Organization (WHO) is calling it “public enemy number one.” But what information do we have that is related to coronaviruses in water and wastewater systems? And what can water- and wastewater-system operators do to protect public health?
Modern water and wastewater treatment systems play an important role in public health protection. With the potential for environmental transmission, water and wastewater operators need to know the potential for survival of this type of virus in water and wastewater treatment systems.
Coronaviruses, named for the crown-like spikes on their surface, were first identified in the mid-1960s. Currently, seven coronaviruses are known to infect people and make them ill. Three of these — MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and COVID-19 — emerged in the last 20 years and are examples of how some coronaviruses that infect animals can evolve to infect humans. COVID-19 is a new variety of coronavirus and is an enveloped, single-stranded (positive-sense) RNA virus.
So, what is the fate of coronavirus in sewage and wastewater treatment plants? Or in the aquatic environment? And should we be worried about the efficacy of water treatment filtration and disinfection processes for coronavirus removal and inactivation?
The short answer: No — if we take proper precautions and risk considerations.
The long answer: This is a new virus without an extensive body of literature on the effectiveness of water and wastewater treatment processes. And real-life experiences will vary due to water quality and treatment plant details.
According to a 2008 University of Arizona study, coronaviruses have not been found to be more resistant to water treatment than other microorganisms such as E. coli, phage, or poliovirus — which are commonly used as surrogates for treatment performance evaluations. Results from bench-scale studies suggest that the survival of coronaviruses is temperature dependent, with greater survival at lower temperatures. Therefore, coronavirus is expected to be reduced in raw wastewater and surface waters in warmer seasons.
How is it transmitted?
Human viruses do not replicate in the environment. For a coronavirus to be transferred via the water cycle, it must have the ability to survive in human waste, retain its infectivity, and come in contact with another person — most likely via aerosols. Findings suggest that COVID-19 can be transmitted through human waste.
Should a major virus pandemic occur, wastewater and drinking water treatment industries would face increased scrutiny. Utilities would need to respond rapidly to minimize occupational and public health risks based on the available evidence. Wastewater effluents would possibly impact recreation, irrigation, and drinking waters. While wastewater treatment does reduce virus levels, infective human viruses are often detected in wastewater treatment plant effluent.
Information for wastewater treatment plant operators
Typically, human waste entering a sewage system is carried through an underground pipe system to a municipal treatment plant. Wastewater treatment plants receiving sewage from hospitals and isolation centers treating coronavirus patients — and domestic sewage from areas of known large contamination — may have elevated concentrations of viruses. Wastewater is treated by a variety of processes to reduce the pollution impacts on nearby receiving waters (lakes, rivers) and disinfected.
Currently, major data gaps exist on the potential role of the water cycle in the spread of enveloped viruses. The lack of detection methods for these strains of viruses is a main reason this type of information is still relatively unknown. Most detection methods are designed and optimized for non-enveloped enteric viruses, and there just isn’t enough information available.
In general, secondary wastewater treatment is credited with removing 1-log (90 percent) of viruses, though broad studies suggest the level of virus removal is highly variable, ranging from insignificant to greater than 2-log removal (99 percent). Because of this variability, the primary process for the inactivation of viruses in wastewater treatment is chemical disinfection (e.g., chlorination) and/or by ultraviolet light.
Drinking water treatment is an effective barrier
Surface-water treatment plants with upstream wastewater impacts are the most susceptible to having coronavirus contamination in the raw water supply during, and after, an outbreak. Viruses are exposed to several potentially inactivating stresses in surface waters, including sunlight, oxidative chemicals, and predation by microorganisms. Generally, enveloped viruses are more susceptible to common drinking water disinfectants than non-enveloped viruses.
Based on published research, water treatment processes that meet virus removal/inactivation regulations are effective for coronavirus control.
For example, drinking water quality guidelines from Health Canada note conventional treatment with free available chlorine can achieve at least 8-log inactivation of viruses in general. Of course, disinfection performance must be continuously monitored (e.g., turbidity, disinfectant dose, residual, pH, temperature, and flow). Optimized conventional filtration can achieve 2-log (99 percent) virus removal and is just one of many processes water treatment facilities incorporate to make our water safe to drink.
Modern drinking water treatment plants are well equipped to remove and disinfect viruses through filtration and disinfection processes.
So now what?
By and large, these viruses are not considered a major threat for the wastewater and water industries due to their low concentrations in municipal wastewater and high susceptibilities to degradation in aqueous environments. According to new OHSA guidance, there is no evidence to suggest that additional, COVID-19-specific protections are needed for employees involved in wastewater treatment operations.
The WHO found that risk communication and community engagement (RCCE) has been integral to the success of response to health emergencies. Action items related to coronavirus include communicating about preparedness measures and establishing a system for listening to public perceptions to prevent misinformation.
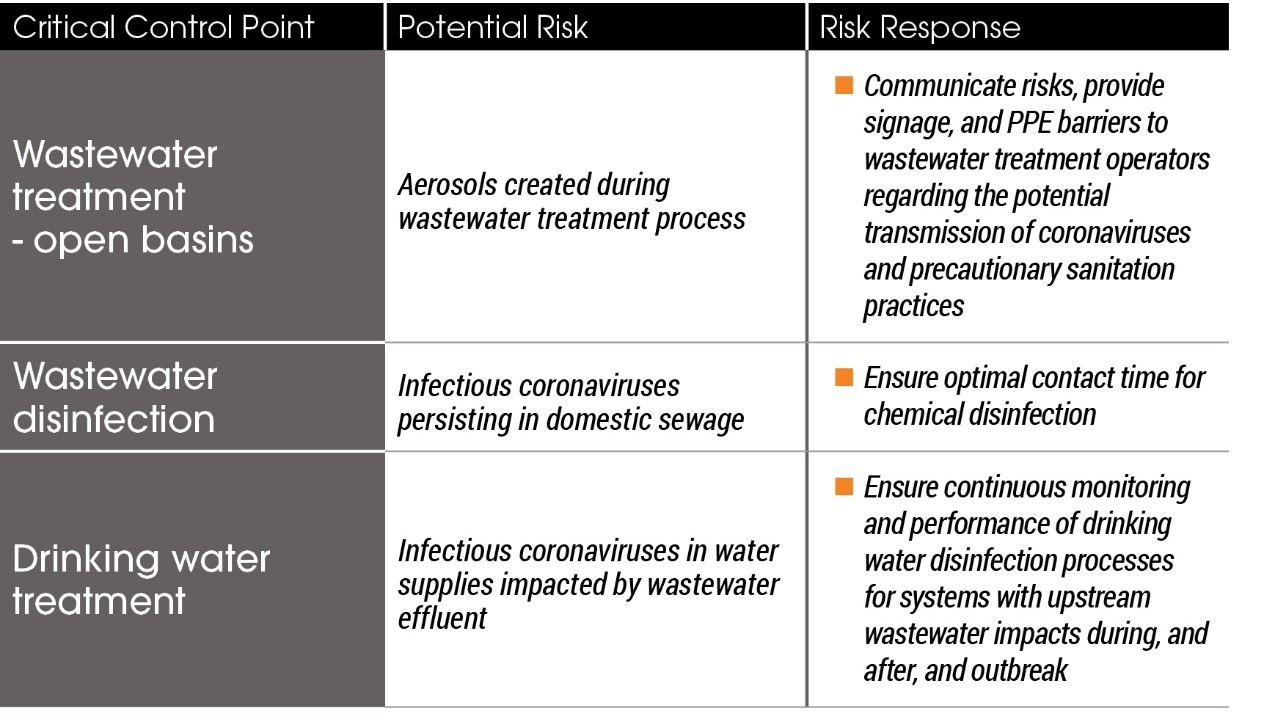
Basic recommendations for treatment-plant operators when dealing with a potential virus outbreak
So far, this virus does not appear to survive well in the environment and can be eliminated effectively by water treatment, especially chlorination, and would pose a minimal risk through drinking water. As the outbreak continues, more water-quality experiments are needed before major conclusions can be drawn on their fate within treatment processes. While this will be tricky, especially as viruses continue to replicate and evolve, quantitative risk assessments should be a top priority for enveloped viruses in wastewater, recreational waters, and drinking water.
Treatment-plant operators can download this white paper for more details on current state of knowledge on coronaviruses as it relates to our practice. For additional reputable and reliable sources of information that are updated frequently with technical guidance, public health information, and the latest research visit the Water Environment Federation’s coronavirus site.
About the authors
Nicole McLellan is an environmental scientist. She has an academic background in environmental microbiology and civil engineering for drinking water treatment performance evaluations.
David Pernitsky is global practice leader for water treatment. He has more than 25 years of environmental engineering experience, managing many challenging studies.
Arthur Umble is Stantec’s global lead for wastewater practice. He develops strategies and provides solutions for complex wastewater treatment challenges.
