SWAN Corner: Scaling 3D Data Quality Alongside Green Recovery
By Victoria Ferguson

Designed to accelerate post-pandemic resilience, boost environmental benefits, and improve customer service en masse, Severn Trent Water launched an infrastructure initiative in 2021: a £566 million (US$766.8 million) Green Recovery program. The time was ripe for the UK’s first ‘smart water data region’, and across Coventry and Warwickshire, the installation of over 150,000 smart water meters and a region-wide lead pipe replacement scheme signaled a step toward smarter, more sustainable water infrastructure.
Working closely with Severn Trent and key delivery partners, MGISS supported the project and its spatial data requirements, ensuring precision and long-term resilience. More than the digitization of asset records, the initiative was set to embed a new standard of geospatial accuracy and accessibility to support enhanced decision-making across the entire water lifecycle.
Lead Replacement And Smarter Water
Alongside smart meter installation, the replacement of thousands of lead pipes presented a massive logistical challenge for the initiative. New supply pipes needed to be accurately mapped, verified, and connected without service disruption, with all asset data required to be captured and uploaded in real-time for long-term operational use.
Traditional mapping methods would not suffice, with speed and precision a must. Depth, orientation, and positional variations were prevalent across legacy records, with many assets with no verified location data at all. With all this in mind, the newly installed assets would need to be captured right down to the centimeter and precisely positioned in a 3D model of the network.
Field Teams Empowered With Real-Time, 3D-Enabled Workflows
Thus, MGISS was positioned in the role of enabling field engineers and contractors to collect, process, and visualize data, using real-time GNSS technology integrated directly into Esri’s ArcGIS Field Maps. MGISS and Severn Trent rolled out high-accuracy data capture workflows using iOS-compatible GNSS devices.
One key component of this workflow was Z-Transform. Developed by MGISS, Z-Transform is a real-time elevation transformation tool that provides consistent and accurate orthometric height data. With many areas using inconsistent vertical datums or lacking in reliable elevation models, Z-Transform was essential for both leak detection and maintenance planning.
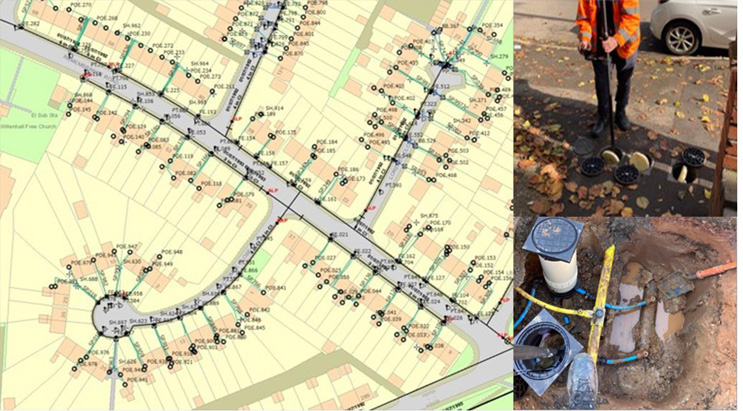
Field teams were therefore equipped to capture the precise location and depth of each new asset as installation progressed. This data was then automatically delivered to Severn Trent’s central GIS environment and was able to support better traceability, faster verification, and more efficient follow-up work scheduling.
This scaling of 3D data quality delivered several critical advantages:
- Reliable leak detection and pressure management: Critical for both proactive maintenance and emergency response.
- Streamlined maintenance planning: Allowing for safer excavation, targeted interventions, and better resource allocation.
- Flood risk reduction and resilience planning: Strengthening climate adaptation strategies.
- Futureproofing for digital twins and AI applications: Laying the groundwork for predictive analytics, automated asset management, and intelligent network simulations.
Elevating 3D data capture enabled Severn Trent to guarantee the value of the Green Recovery program, extending beyond initial asset delivery and enabling smarter, faster operations. By focusing on 3D-enabled, high-precision data capture, teams could deliver immediate project goals. This meant that relocating problems would become a much easier task in the future.
A Culture Shift Toward Data Accountability
The success of this smart water data program lay not only with the technology employed, but with a shared commitment to quality. Field operatives needed to be trained on how to use devices effectively, confident in their ability to validate data on-site and the knowledge that the data was captured correctly.
In reducing data rework, eliminating the need for return visits, and ensuring real-time feedback, a culture of data accountability was established.
Innovation Across The Network Lifecycle
The program trialed a range of innovative detection and monitoring technologies alongside its spatial workflows, including non-invasive identification methods for pipe materials on the customer side of the stop tap. Acoustic-based techniques were employed to identify whether customer-side pipework was lead, copper, or plastic, without the need for excavation or home entry.
Integrated with digital mapping tools, these innovations were key to providing a more complete view of the asset environment while removing disruption to the customer.
Over 17,000 lead pipe connections were successfully replaced between October 2022 and August 2024, covering more than 43,000 meters of newly laid infrastructure — each one captured, geolocated, and uploaded in real time to Severn Trent’s systems.
Smart Metering Needs Smart Mapping
Severn Trent knew that early investment in geospatial accuracy and real-time data flows would be the key to success in the Green Recovery program, with benefits extending well beyond immediate installation. Like any utility looking to modernize at scale, a smart network needs a trusted, spatially-enabled bedrock.
A Resilient, Data-Rich Future
With the dual pressures of climate change and aging infrastructure working against water companies in the UK and beyond, programs like this — holistic, data-driven, and transformative — may be the blueprint for sector-wide change. There is growing momentum in this direction, as MGISS see day in and day out, from proactive maintenance in everything from sewers and drainage systems to flood risk reduction and automation through digital twinning and AI.
Spatial accuracy is the powerhouse of a smart water strategy, working from project inception to ensure reliable operations, efficient maintenance, and sustainable growth. The experience in Coventry and Warwickshire has shown that with the right tools, training, and commitment, it’s possible to deliver large-scale change that’s not only innovative and effective, but enduring.
Victoria Ferguson is Client Insight Specialist for MGISS and is responsible for interviewing clients and crafting insight and intel into case studies and good news stories.
SWAN, the Smart Water Networks Forum (SWAN), is the leading global hub for the smart water sector. A UK-based non-profit, SWAN brings together leading international water utilities, solution providers, academics, investors, regulators, and other industry experts to accelerate the awareness and adoption of “smart,” data-driven solutions in water and wastewater networks worldwide. Learn more at www.swan-forum.com.
